Harness the Benefits of Biogas
Learn how biogas systems can benefit you, your business, and your community.
Biogas systems recycle decomposable waste– like manure, food waste, wastewater solids and other organic material–into energy and fertilizer.
In the U.S., there is an urgent need to manage millions of tons of food, water and animal waste. The benefits of biogas systems include recycling all these materials and transforming them into renewable energy and soil fertilizers.
Each year the United States produces:
- Over 120 million tons* of farm animal manure
- 12 million tons* of municipal wastewater biosolids (sludge)
- and sends more than 24,000,000 tons of inedible food waste to landfills.
In addition, at least 470 landfills currently flare gas that could be repurposed.
The ABC estimates that about 17,000 additional biogas projects could be built to:
- convert waste into valuable domestically-produced energy
- improve crop yields and nutrients
- preserve landfill space and
- create good-paying jobs
These new biogas systems hold the potential to produce up to 29 gigawatts of 24/7 electricity. They would also create about 900,000 short-term construction jobs and 45,000 permanent operations jobs, plus thousands more indirect supply chain jobs.
(* dry tons)
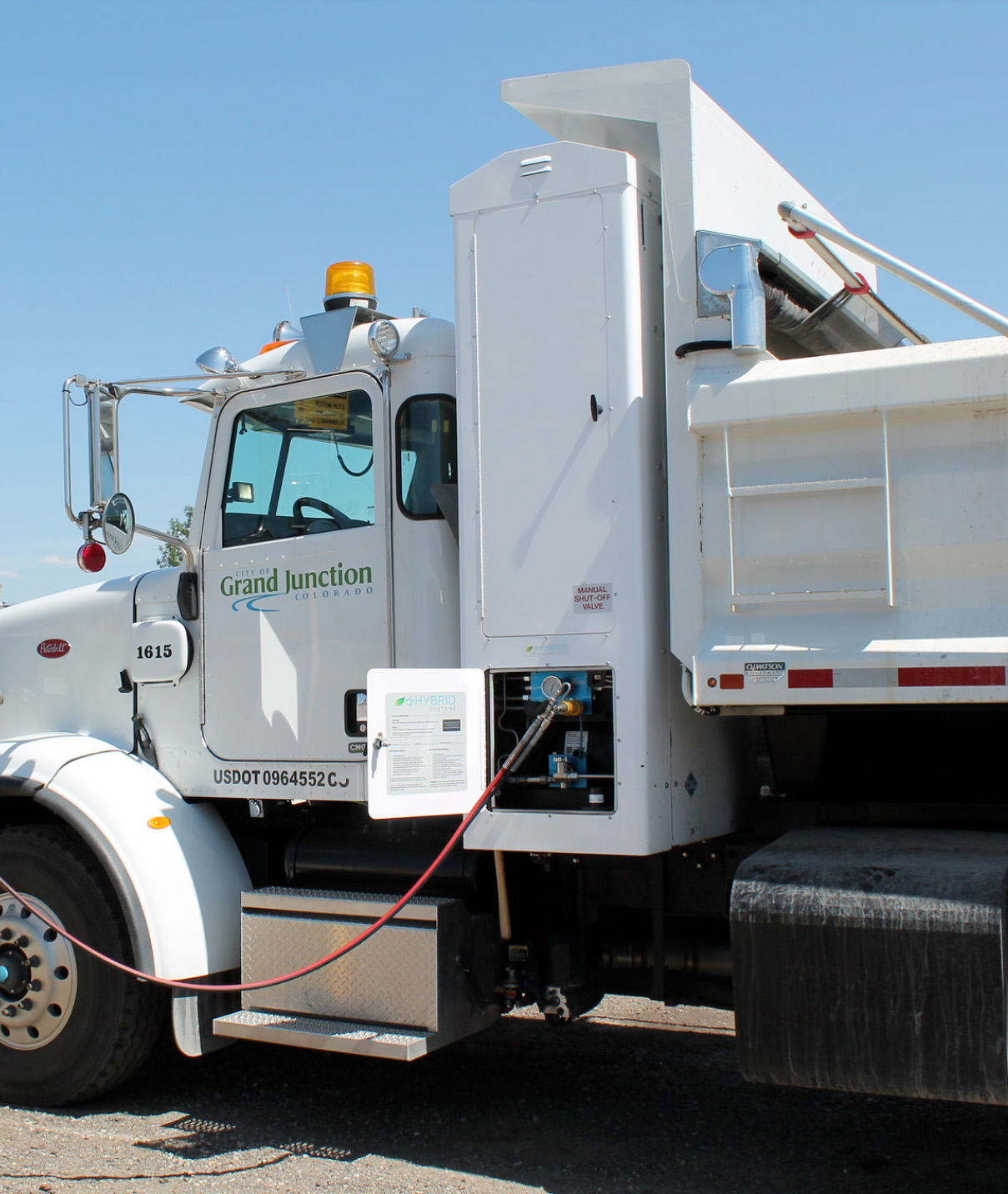

Energy Benefits
- A renewable source of energy that is a direct replacement for non-renewable, carbon-intensive fossil fuels
- Produces renewable energy 24/7/365, with a reliability rate of 95%–in comparison, the average reliability rate for solar power is 25% and 35% for wind power
- Biogas supports distributed generation of energy, which means lower transmission and transportation costs as well as reduced impact and higher reliability of electrical grids
- Provides power in minutes, reducing the need to turn on fossil- fueled power plants to meet peak demand
- Can be used interchangeably with natural gas for heating, electricity, and the production of renewable transportation fuels.
- Helps large companies and institutions reduce fossil fuel use, and decrease their carbon footprint
- Greatly reduces emissions from carbon-intensive industries like industrial manufacturing.
Economic Benefits
- Turns the expense of waste treatment into a revenue-generating opportunity for farmers and rural communities
- Creates new revenue streams in rural America, helping farmers find new sources of income when commodity prices dip.
- Can reduce farm costs for animal bedding and fertilizer.
- Drives economic growth and new local jobs in construction, engineering, project management and more
- Reduces the volume of waste and lowers costs for facilities like wastewater plants
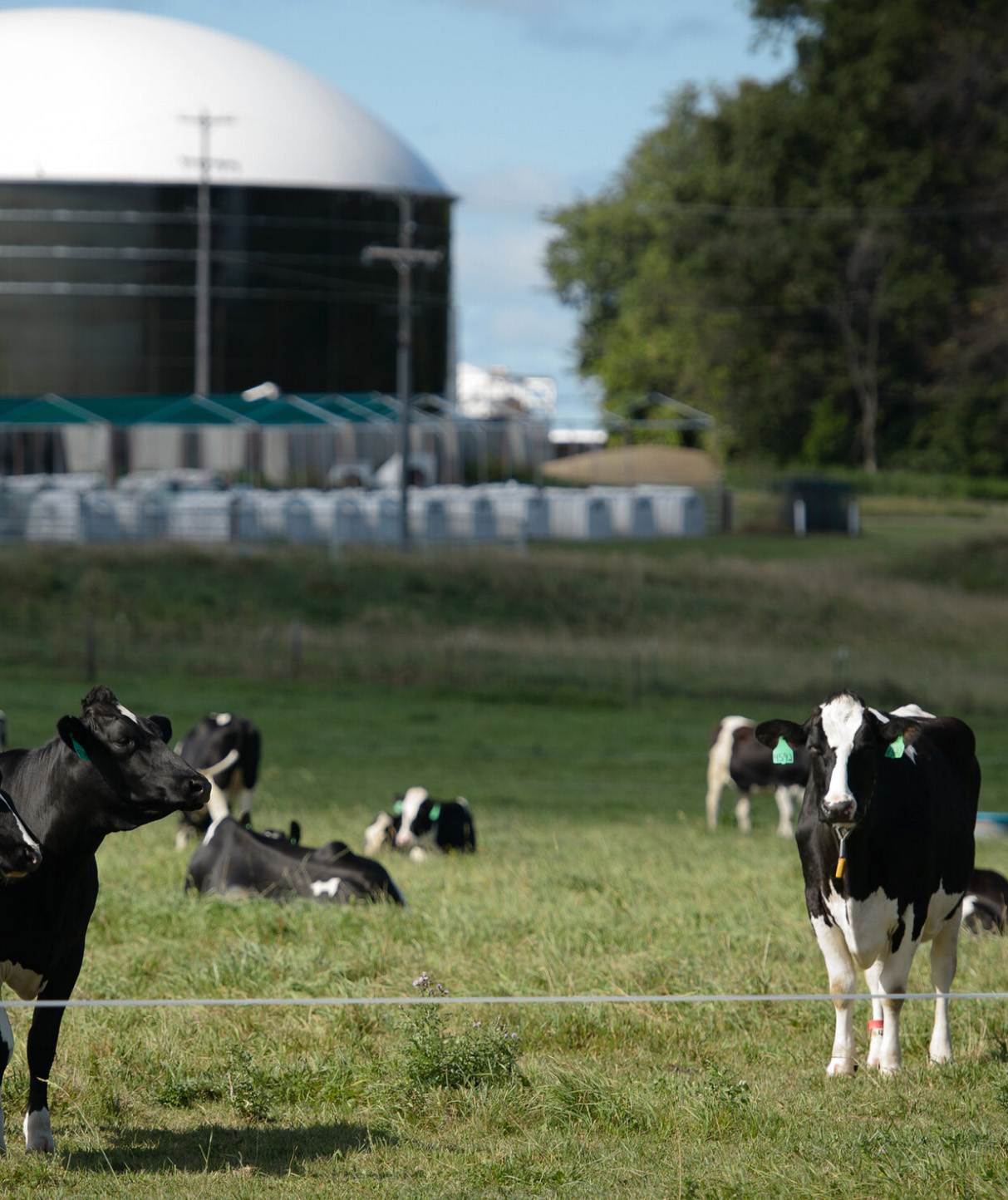


Environmental Benefits
- Recycles manure and kills odors and pathogens, while producing renewable energy and non-synthetic fertilizer.
- Help assist the natural cycles of recycling to farming
- Reduces greenhouse gas emissions by moving manure from open lagoons to an airtight biogas system.
- Reduces carbon emissions in transportation by at least half compared to fossil fuels
- Replacing even a small percentage of non-renewable fuel with renewable biogas or renewable natural gas can drastically reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Unlike using raw manure as fertilizer, anaerobically digesting manure creates an opportunity to separate out nutrients like ammonia and nitrogen before field application, which helps keep them out of waterways
- Can be used to replace costly synthetic fertilizers with natural fertilizers shown to boost plant growth.
Biogas Industry Statistics
Today, the U.S. has close to 2,500 sites producing biogas in 50 states, including more than 600 farms, 1,189 water resource recovery facilities, 113 stand-alone systems that digest food waste and 583 landfills.

The U.S. currently has the potential to build 17,000 new biogas systems, which would create significant economic, environmental and energy benefits.

Building out the U.S. biogas infrastructure could produce an additional 204 billion kilowatt-hours of electricity per year (19 million homes), 185 billion BTU of renewable heat per hour (21 million homes), or fuel for vehicles equivalent to 13.5 billion gallons per year (31 million vehicles).

Building out the U.S. biogas infrastructure could generate at least $450 billion in new capital deployment for construction activity resulting in 900,000 short-term construction jobs and 45,000 permanent jobs.
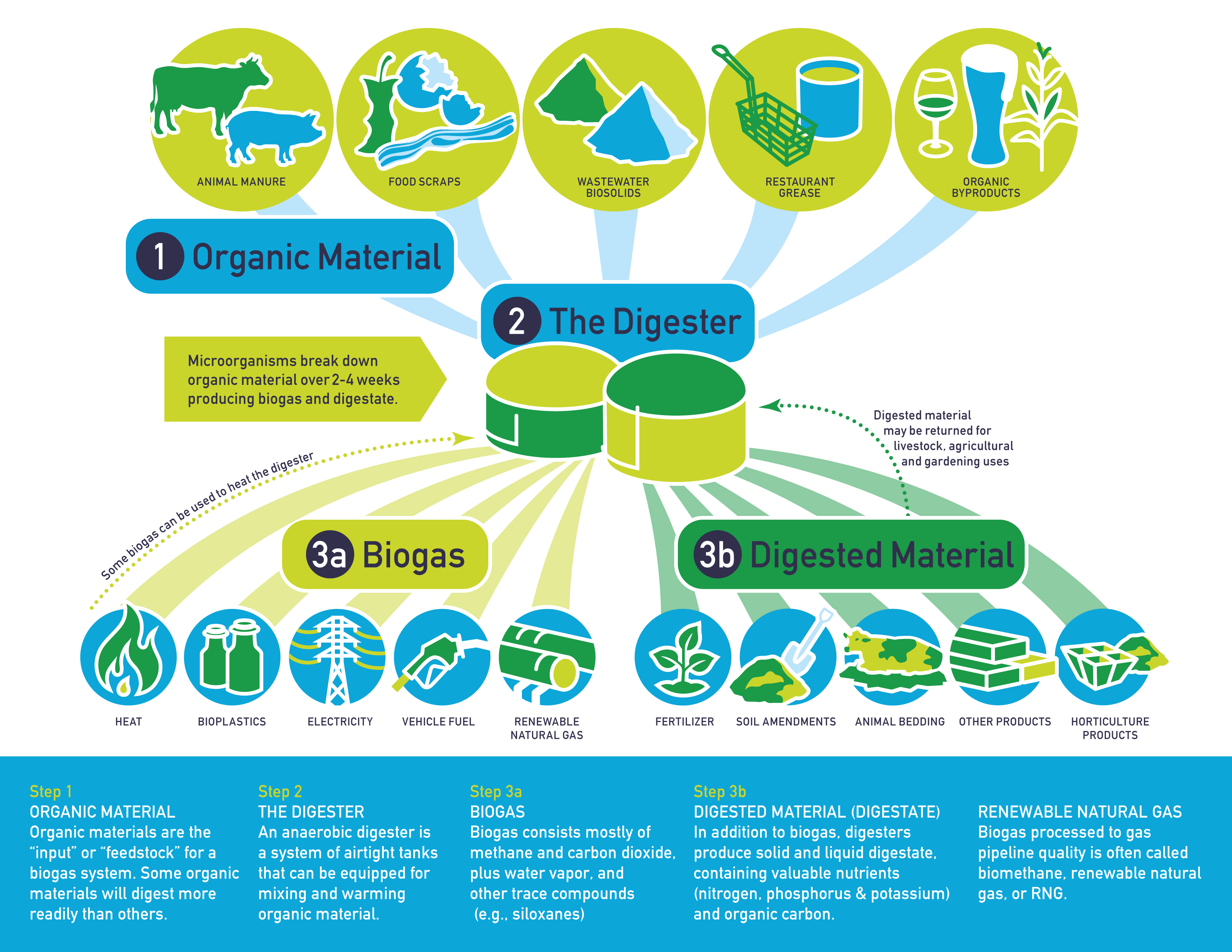
How Biogas Systems Work
Select each step below to learn how biogas systems work
Step 1
1 ORGANIC MATERIAL
Organic materials are the “input” or “feedstock” for a biogas system. Some organic materials will digest more readily than others.
- Animal Manure
- Food Scraps
- Wastewater Biosolids
- Restaurant Grease
- Organic Byproducts
Step 2
2THE DIGESTER
An anaerobic digester is a system of airtight tanks that can be equipped for mixing and warming organic material.
Step 3a
3aBIOGAS
Biogas consists mostly of methane and carbon dioxide, plus water vapor, and other trace compounds (e.g., siloxanes)
- Heat
- Bioplastics
- Electricity
- Vehicle Fuel
- Renewable Natural Gas
Some biogas can be used to heat the digester!
Step 3b
3bDIGESTED MATERIAL (DIGESTATE)
In addition to biogas, digesters produce solid and liquid digestate, containing valuable nutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus & potassium) and organic carbon.
- Fertilizer
- Soil Amendments
- Animal Bedding
- Other Products
- Horticulture Products
Digested material may be returned for livestock, agricultural and gardening uses!
RNG
RENEWABLE NATURAL GAS
Biogas processed to gas pipeline quality is often called biomethane, renewable natural gas, or RNG.
Additional Resources
Biogas Market Snapshot
This one-pager includes high level information on the current state of the biogas industry and potential of biogas in the United States.
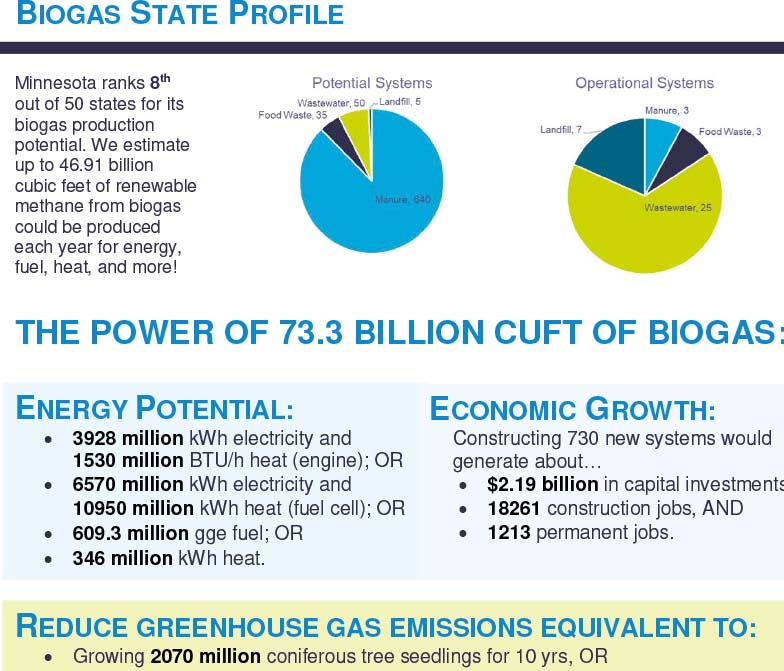
State Profiles
This one-pager includes high level information on the current state of the biogas industry and potential of biogas in the United States.

Biogas Definitions
A list of words you may find throughout this website and other biogas resources with their definitions.

Biogas Acronyms
A list of acronyms you may find throughout this website and other biogas resources with their definitions.