$1.8 billion was invested in new projects last year, according to numbers just released by the American Biogas Council
February 13, 2024 – WASHINGTON – Newly-released data from the American Biogas Council (ABC) indicates that 2023 was the third year of record growth across the U.S. biogas industry,[1] with nearly 100 new projects coming online last year— representing $1.8 billion in capital investments. ABC expects this growth to continue into 2024, with more than 100 new projects already projected to go into operation this year.
The growth of the U.S. biogas industry goes beyond increased domestic investments and renewable energy production. It also proportionally reduces methane emissions and spurs construction of recycling infrastructure, which will benefit Americans for decades to come.
Biogas systems recycle organic waste, capturing methane that would have been produced without them, and turning it into renewable energy—while reducing the use of fossil fuels for energy and fertilizer. These systems are a value-packed solution to addressing the urgent need in the U.S. to manage millions of tons of food, water and animal waste. At the same time, these systems prevent tons of carbon-related emissions from entering the air, keep nutrients from polluting waterways, create healthier soils with natural, non-fossil fuel-based fertilizers, and produce reliable, baseload or dispatchable, renewable energy.
After processing, biogas is most often used as a renewable substitute for natural gas, for electricity and for heat that varies in carbon reduction from 50% to 700% compared to fossil fuels.
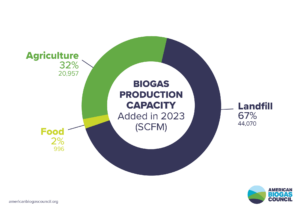
In 2023, 96 new biogas projects[2] became operational in the U.S., pushing the total number of active U.S. biogas projects to 2,251, which represents $39 billion in capital investment. The new projects produce 66,000 standard cubic feet per minute (SCFM) of biogas—an electricity equivalent to 4,000 football fields of solar panels, to powering 600,000 homes or to eliminating 600,000 gasoline cars from the road.
“This is an exciting time of growth for a renewable energy sector that is directly responsible for methane emission reductions,” said Patrick Serfass, executive director of ABC. “As the biogas industry expands, so, too, does our capacity to capture methane emissions that would otherwise be emitted from organic waste. We can simultaneously use that captured methane to displace other emissions from fossil fuels that are used for energy and making fertilizer. It’s a win-win that often results in negative carbon emissions.”
“Most other renewables can only get to a carbon intensity of net zero. If a company buys renewable natural gas made from biogas with a carbon intensity six times lower than natural gas, it only must replace 1/6 of its gas usage to reduce all of its carbon emissions from that gas,” said Serfass.
Landfill gas leads both investment dollars and biogas output
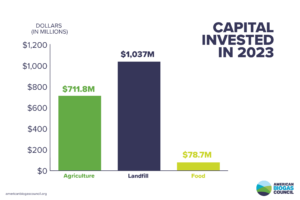
Landfill gas (LFG), the natural byproduct of the decomposition of organic material in landfills—also called biogas—continues to dominate in terms of both total investment and biogas output. Instead of allowing LFG to escape into the air, it can be captured, converted and used to displace fossil fuel emissions. The U.S. currently has 566 LFG projects, including 23 new projects added in 2023. This growth accounts for 57% of 2023 capital investments and 67% of new biogas production capacity.
Significant gains in agriculture, food waste
While the growth of the landfill gas sector was voluminous in terms of both dollars and biogas, 2023 saw only 4-5% growth in that sector. In comparison, the growth in the agricultural sector was 13.4%, or nearly three times greater. Seventy new farm-based projects came online in 2023, contributing 21,000 SCFM of additional biogas output and resulting in capital investments exceeding $700 million.
Renewable natural gas (RNG) cluster projects contributed most to the growth and to lowering the cost per project. Cluster projects are generally characterized by multiple farms with at least one anaerobic digester linked together by one common, central gas processing and conditioning facility to turn the biogas into RNG. The lower per-project costs are also impacted by the fact that many cluster projects use lagoon-style biogas systems (a covered, in-ground, lined pit), which are more cost-efficient and therefore less expensive than the more commonly used engineered tanks.
Significant growth continues in the food waste sector, on par with landfill sector growth. Three new stand-alone food waste biogas projects became operational in 2023, adding an extra capacity of 996 SCFM, with 10 more facilities scheduled to launch in 2024.
Renewable electricity from biogas remains dominant, but growth is in RNG
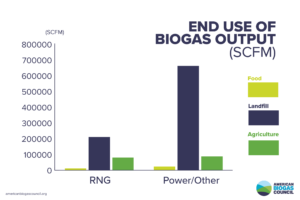
While power projects that make renewable electricity from biogas account for 69% of all biogas produced in the U.S., biogas RNG projects represented 91% of all new projects that came online in 2023. This mainly stems from policies such as the federal Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) and the California Low Carbon Fuel Standard (LCFS), which promote using renewable fuels to replace fossil transportation fuels and to eliminate emissions.
Currently, it’s often easier to develop profitable RNG projects in the U.S. because the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is suppressing participation of biogas systems in the RFS when systems provide electricity to battery electric vehicles or hydrogen to fuel cell electric vehicles.
While impressive growth in the U.S. biogas industry continues, only roughly 20% of possible projects have been built. ABC counts at least 15,000 new systems that could be built—compared to 2,251 operational today, based on the millions of tons of organic material in the U.S. produced annually by humans and animals. As the biogas industry continues to expand, significant economic, environmental and energy advantages are unlocked.
The collective impact encompasses several benefits, including carbon reduction, improved water quality, soil health enhancements and reliable, renewable energy. Embracing biogas systems signifies a proactive step toward a sustainable future, where environmental stewardship and resource efficiency converge for the betterment of society and the planet.
###
About the American Biogas Council
The American Biogas Council is the voice of the U.S. biogas industry dedicated to maximizing carbon reduction and economic growth using biogas systems. We represent more than 400 companies in all parts of the biogas supply chain who are leading the way to a better future by maximizing all the positive environmental and economic impacts biogas systems offer when they recycle organic material into renewable energy and soil products. Learn more online at AmericanBiogasCouncil.org, X @ambiogascouncil, and LinkedIn.
[1] Excludes the wastewater treatment sector which represents approximately 1,000 biogas-producing facilities.
[2] A farm with at least one digester is counted as a single project.